Theory Test Hazard Awareness
To learn all about the Hazard Awareness category, watch the video or read the article below.
The theory test featuring questions from this category is at the bottom of the page.
Attitude Means
- Your frame of mind when you are driving
- How you react when you meet road hazards
- How you behave towards other drivers
Topics Include
- Anticipation – using forward planning in order to avoid rash, unsafe decisions
- Tiredness – knowing how tiredness can affect you whilst driving
- Attention – remaining alert and looking for problems ahead
- Reaction Time – understanding you need time to react
- Drugs and Alcohol – knowing how drugs and alcohol affect you when driving
- Hazard Awareness – recognizing potential hazards and how to deal with them
- Speed & Distance – understanding the correct speeds to use in all driving situations.
In general, whenever you drive towards a hazard you should reduce your speed.
Hazards are anything that may make you slow down, change direction or stop.
Again, if your stuck for an answer always select the safest option.
Alcohol
You can drink a small amount of alcohol and still legally drive. However, in the context of the theory test, no alcohol is always better, and the right answer when one of the options.
Drinking alcohol will give a driver:
- Less control
- A false sense of confidence
- Poor judgment of speed
- Reduced co-ordination
- Reduced concentration
- Poor judgment
- Increased confidence
- Get a conviction for driving whilst unfit through drink or drugs and your car insurance premium will rise significantly.
Illness
- If you have any illness that is likely to negatively affect your driving ability then don’t drive.
- Taking a medicines that might impact negatively on your driving i.e. make you feel drowsy? Then consult your doctor to make sure you can safely drive.
- Always read the label of any medicine, even cough medicine.
- If you start to suffer from ill health, which affects your driving, you should inform the licensing authority.
Tiredness
When driving, if you start to feel tired you should always find a safe, convenient place to stop and rest. If no such place is immediately available you should open a window and allow a good supply of fresh air into the car.
On a long journey always take regular rest breaks. Regular stops help maintain concentration.
When driving on a motorway if you start to feel tired you should leave the motorway at the next exit, find a safe place to stop and rest.
Concentration
Maintaining high levels of concentration is essential for road safety. Whenever a driver’s concentration levels dip or are under threat they should stop and rest until they are capable of maintaining the high levels of concentration needed to drive safely.
Loss of concentration can be caused by:
- Looking at maps
- Listening to loud music
- Using a mobile phone
- Tiredness
Cyclists
- Give cyclists plenty of room. They may wobble or swerve to avoid drains or potholes.
- When travelling in slow traffic, before you turn left, check for cyclists filtering through the traffic on your left.
- At junctions or traffic lights give them time to turn or pull away.
Motorcyclists
Look out for motorcyclists, especially when you’re:
- emerging from a junction
- turning into a road on your right
- changing lanes or moving out to overtake.
Other Facts to Know
- A driver does something to upset you. You should try not to react, ignore the error and stay calm.
- A flashing amber beacon on a vehicle signifies that the vehicle is slow moving.
- If your eyesight becomes poor you should tell the licensing authority.
- An automatic car uses ‘kick-down’ for quick acceleration.
- In areas where there are traffic calming measures you should drive at a reduced speed.
- The only time you are permitted to use hazard warning lights while moving is if you are on a motorway or dual carriageway and you need to warn other road users of a hazard ahead.
- At a junction where the traffic lights have failed you should be prepared to stop for any traffic.
- Convex mirrors are slightly curved. This allows a wider field of vision.
- Low bridges – give way to buses and lorries when approaching them. In order to drive under the bridge tall vehicles will have to take up position in the centre of the road, as this is where the highest point of the bridge is.
- When following a cyclists be aware that the cyclist may swerve out into the road.
- An elderly person’s driving ability could be affected because they are unable to react quickly. Be patient with them.
- On a long journey it is recommended that you take breaks of at least 15 minutes for every two hours of driving.
- At a junction where traffic lights have failed, you must be prepared to stop for any vehicle.
- When driving passed parked cars at the side of the road look out for car doors opening and children running into the road from between the parked cars.
- When approaching traffic calming measures you should reduce your speed.
- On a two-way road with three lanes, the middle lane is used for overtaking. If you intend to use the middle-lane to overtake be careful, an approaching vehicle may be about to also use the lane to overtake.
- Never overtake when your view ahead is blocked, when approaching a junction, when turning left shortly afterwards.
- Never reverse or do a u-turn in a one-way street.
- School buses may stop at places other than signed bus stops.
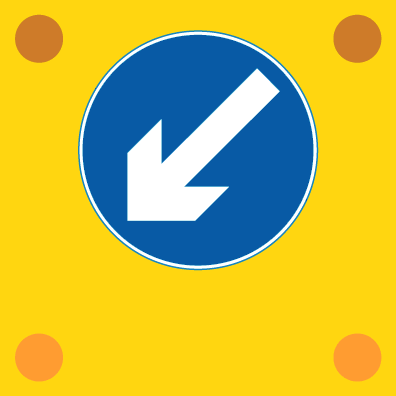
This sign is found on slow-moving or stationary works vehicles. Overtake on the left, as indicated by the arrow.
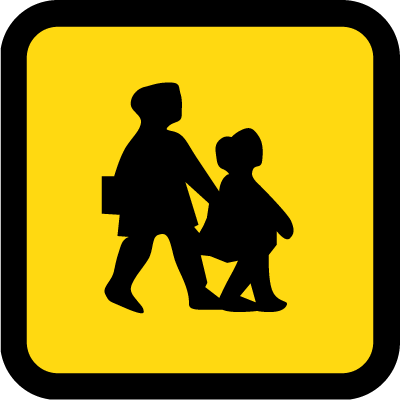

This sign on a vehicle indicates that the vehicle is a school bus.
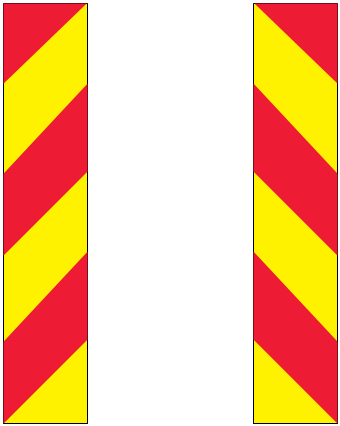
These warning markers are fitted to vehicles over 13 metres long, large goods vehicles and rubbish skips placed in the road.
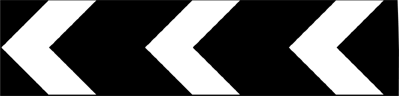
This sign means a sharp deviation to the left (right if the arrows face right)
